Urinary Tract Infection UTI Overview
Urinary tract infections (UTI) are more common in women. They can occur anywhere in the urinary system, but most infections involve the lower urinary tract – the bladder and the urethra.
A bladder infection may cause pelvic pain, increased urge to urinate, pain with urination, and blood in the urine. A kidney infection may cause back pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever.
Common treatment for UTIs is with antibiotics.
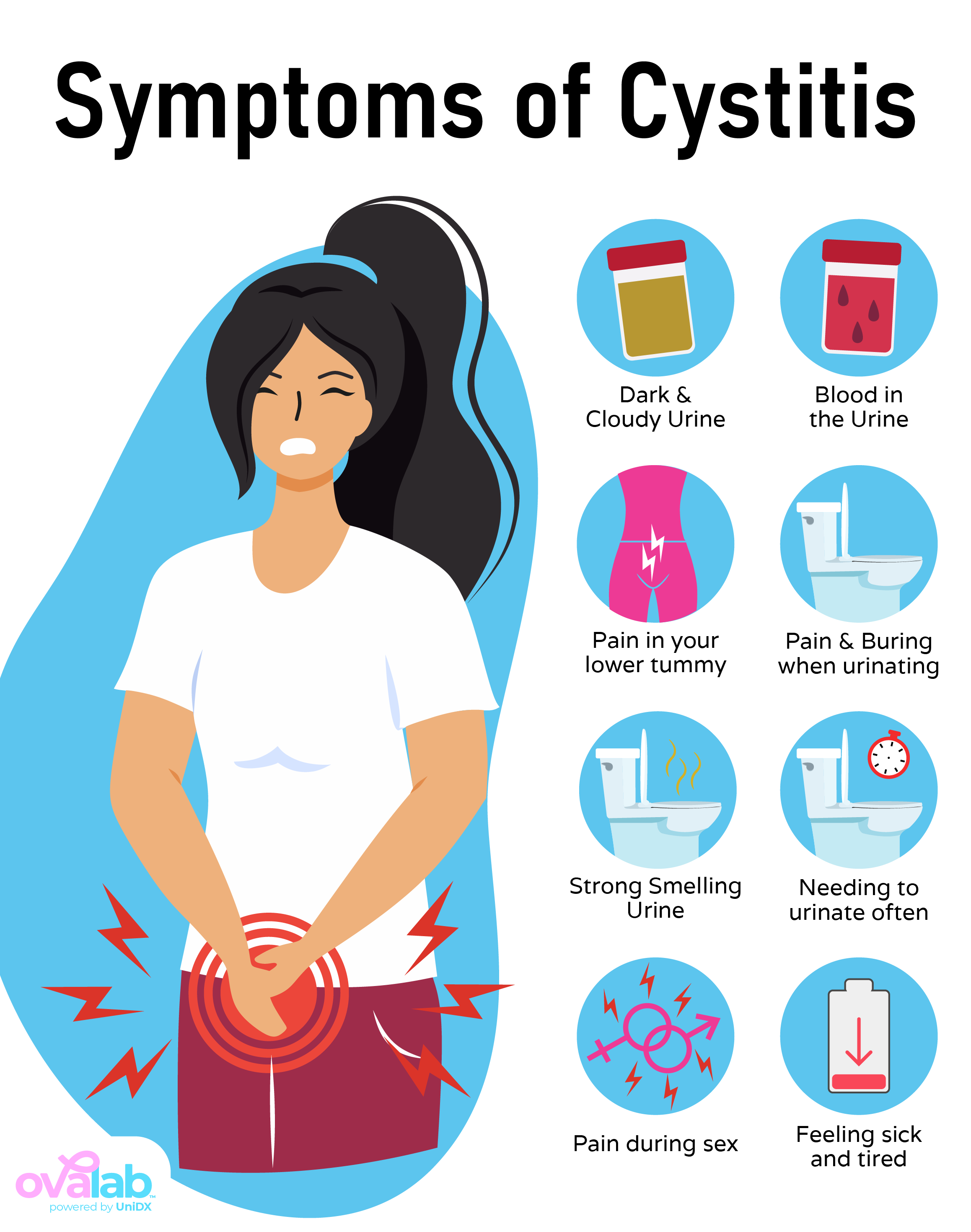
What Are the Symptoms of a UTI?
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate frequently
- A painful, burning sensation when urinating
- Pain in the bladder or anywhere along the urinary tract
- Passing small amounts of urine
- Cloudy urine
- Urine that looks red, pink or dark (blood in the urine)
- Strong smelling urine
Can I get a UTI from having sex?
Women’s anatomy makes them much more prone to getting UTIs after having sex. The opening of the urethra is in front of the vagina. During intercourse, bacteria near the vagina can enter the urethra.
What reduces the Risk of UTIs?
Drink plenty of fluids, especially water. Helps flush bacteria from your urinary tract before an infection can begin.
Drink cranberry juice. May help prevent UTIs.
Wipe from front to back. Helps prevent bacteria from spreading to the vagina and urethra.
Urinate immediately after intercourse. Also, drink a full glass of water to help flush bacteria.
Wash the skin around the urethra, especially after intercourse.
Empty your bladder as soon as you feel the urge, about every 2 to 3 hours.
Avoid feminine products. They can irritate the urethra.
Change your birth control method. Diaphragms, or unlubricated or spermicide-treated condoms can all contribute to bacterial growth.